Pure Axial Loading
A member is said to be under pure axial loading, when two
equal and opposite load act along the axis of the member in such a way that its
magnitude remains constant throughout the length of the member. In this, we
have assume that member is a prismatic bar (i.e. dimension are same throughout the structure).
 |
| Pure Axial Load |
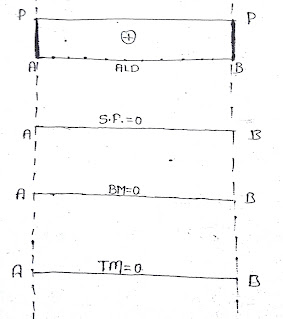
Under axial loading condition we found
that bending moment, shear force and twisting moment are zero.
 |
| SFD & BMD Diagram |
There are many method in strength of
material to obtains the stress occurred on member due to application of pure
axial loading, here we have considered stress calculation as per “section method” which say that load
acting to any cross section is equal to algebraic sum of corresponding load
either on the left hand side of the cross section or on the right hand side of
the cross section of the member.
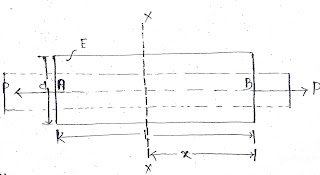
We see in the below image that at the section x-x axial load is “P” and Shear force, bending moment and twisting moment is “0”.
Axial load is also independent of location of section x-x which signify that axial load is constant, so we can say that member is under pure axial load. We can calculate stress and deformation caused due to axial load using below equation.
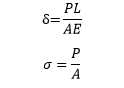 |
| Stress and Deformation |
Above equation is only applicable when it
satisfied following condition.
- Member should
be prismatic whose magnitude remains constant throughout its length.