Structural steel design is an area of knowledge of structural
engineering where we used to design steel structures. The structures can range
from schools to homes to bridges. Structures such as buildings, bridges,
aircraft and ships are all examples which comes under steel structure.
The
effects cause on structure due to
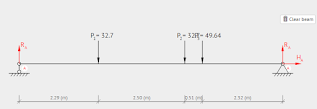
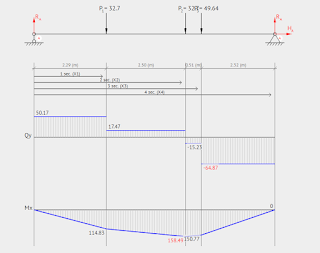
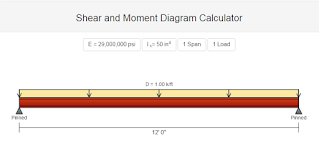
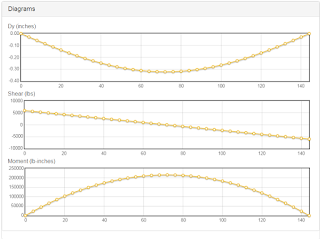
application of load is determine through structural analysis Strength of materials
is the branch of engineering which deals with the study of structural design. Engineering
software such as STADD Pro, TEKLA , SACS, ANSYS
etc. are used to analyze their strength.
Basically Steel structure is steel
construction material with a unique
profile and a specific shape or
cross section with certain standards of chemical composition and mechanical
properties.
The American Institute of Steel
Construction (AI SC), Inc. publishes the Steel Construction Manual (Steel
construction manual, or SCM), which is currently in its 14th edition.
Structural engineers use this manual in analyzing, and designing various steel
structures.
The mentioned link will give you
the complete description of AISC 's structural steel shapes in the US and will provide you the reference to
determine the availability and engineering design data of specific structural
steel shapes.
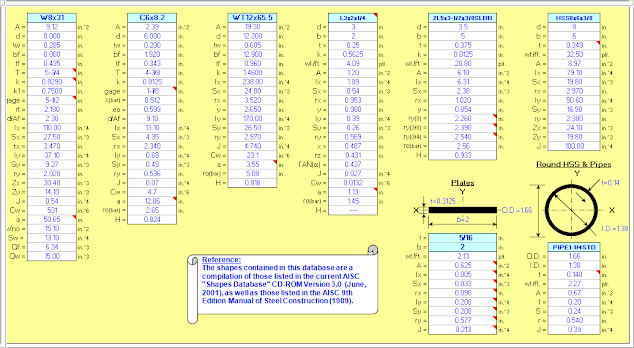
(Click Here) Link:- AISC Structural Shapes
Click above link to find ASIC Structural Shape Properties
Source:-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wikihttp://www.engineersedge.com